A class to create separate threads. More...
#include <mcs.hh>
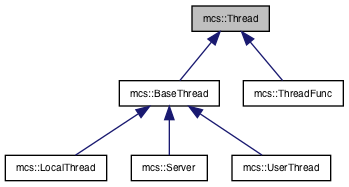
 Inheritance diagram for mcs::Thread:
Inheritance diagram for mcs::Thread:Public Member Functions | |
| Event * | error () |
| Return last error message. More... | |
| int | id () |
| Returns the Thread object identificator. More... | |
| Thread * | parent () |
| Returns the address of the parent. More... | |
| void | start () |
| Start a new thread in the joinable state. More... | |
| void | startDetached (bool selfDelete=false) |
| Start a new thread in the detached state. More... | |
| int | state () |
| Return the state of the thread. More... | |
| void | stop () |
| Stop thread execution. More... | |
| Thread (int id=0, Thread *parent=NULL) | |
| Declared to avoid using of default copy constructor. More... | |
| virtual | ~Thread () |
| Destructor. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | final () |
| Finalization method. More... | |
| virtual void | initial () |
| Initialization method. More... | |
| virtual void | notify (int id, Thread *ref) |
| A method called from child threads to notify their termination. More... | |
| virtual void | run () |
| Body of the thread execution. More... | |
| void | set_cancel_state (bool cancel) |
| Set cancellation state for current thread. More... | |
| void | test_cancel () |
| Test if a cancellation request is pending. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Event * | lerror |
| Last error. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| bool | checkTerminating () |
| Starting point for the separate thread. More... | |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| static void | cleanup_Handler (void *This) |
| Static wrapper around final(). More... | |
| static void * | RunThread (void *args) |
Private Attributes | |
| bool | detached |
| Tell if the thread is to be created in the detached state. More... | |
| int | lid |
| General purpose Thread identifier. More... | |
| Thread * | lparent |
| Reference to parent Thread object, if any is given in the constructor. More... | |
| int | lstate |
| State of the object, see state() method. More... | |
| pthread_t | lthrID |
| System's thread identifier. More... | |
| bool | selfDelete |
| Tell if the object should delete himself once the thread is terminated. More... | |
Detailed Description
A class to create separate threads.
This class let you run code in a separate thread. You can derive this class and overload its virtual method run(), this will be the thread body being executed when you start the new thread.
A thread can be started from the parent thread in two ways:
- in the joinable state (using the start() method): this way another thread (for example the parent) can stop the newly created thread while it is running.
- in the detached state (using the startDetached() method): this way the thread can only terminate by itself.
The child thread will always execute three methods: initial(), run(), final(). These are virtual methods, so you can overload them in derived classes. The initial() method can be used to perform initialization tasks. It is useful because it is guarranteed that the start() (or startDetached()) method won't return until the initial() method has returned, so the main thread knows that the separate thread is already running. The run() method is the body of the separate thread execution. A thread can terminate in three different ways:
- the control reach the end of the overloaded run() method;
- an exception is thrown inside the overloaded run() method;
- the stop() method is called from another object/thread (applicable only if the thread has been started in the joinable state).
The final() method can be used to free resources allocated by the separate thread. This method is useful because a thread can terminate either by returning from the run() method, or because it is stopped from another thread. In any case the final() method will be executed in the separate thread, so it can be used to free allocated resources.
If the adress of a parent object has been provided in the constructor call, then it will be notified of thread termination (see notify() method), after the final() method has been executed.
This class provide the state() method which tells in which "state" of its life-cycle a thread is. The value of the state can be one of the follows:
- MCS_STATE_CREATED: the object has been created but the separate thread has not been started.
- MCS_STATE_RUNNING: the separate thread has executed initial() method and it is executing the run() method.
- MCS_STATE_TERMINATING: the run() method has returned or the stop() method has been called, and the thread is going to execute the final() method and eventually notify its parent of thread termination.
- MCS_STATE_END: the separate thread has executed the final() method, (eventually) notified its parent and terminated its execution.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Thread()
| mcs::Thread::Thread | ( | int | id = 0, |
| Thread * | parent = NULL |
||
| ) |
Declared to avoid using of default copy constructor.
- Warning
- This constructor is declared but not implemented. If you try to use it you will get a compilation error.
Declared to avoid using of default assignment operator.
- Warning
- This operator is declared but not implemented. If you try to use it you will get a compilation error.
Constructor.
◆ ~Thread()
|
virtual |
Destructor.
You should avoid destroying Thread objects unless you are sure that the separate thread has terminated.
A good choice to destroy Thread objects is to place a "delete" statement inside the notify() method, otherwise you can start the thread in the detached state (with the startDetached() method) and set the "selfDelete" flag to true.
Member Function Documentation
◆ checkTerminating()
|
private |
◆ cleanup_Handler()
|
staticprivate |
◆ error()
◆ final()
|
protectedvirtual |
Finalization method.
This method is executed inside the separate thread once the thread has terminated (the run() method has returned or another thread called the stop() method).
You can use this method to perform finalizations like memory cleanup, objects destructions, etc...
◆ id()
| int mcs::Thread::id | ( | ) |
◆ initial()
|
protectedvirtual |
◆ notify()
|
protectedvirtual |
A method called from child threads to notify their termination.
If the address of a parent thread is provided in the constructor then the child can notify its parent of its termination through this method.
Note that this method will always be ran inside the child thread.
This method can be used to destroy Thread objects once their thread is terminated, for example:
- Parameters
-
id Thread identifier of the terminating thread. ref Address of the Thread object whose thread is terminated.
Reimplemented in mcs::Server.
◆ parent()
| Thread * mcs::Thread::parent | ( | ) |
◆ run()
|
protectedvirtual |
Body of the thread execution.
When the new thread starts it will automatically execute the code in the run() method. This is the method you should overload in derived class to do the work you need.
Thread will be terminated once this method returns.
Reimplemented in mcs::Server, mcs::LocalThread, and mcs::UserThread.
◆ set_cancel_state()
|
protected |
◆ start()
| void mcs::Thread::start | ( | ) |
◆ startDetached()
| void mcs::Thread::startDetached | ( | bool | selfDelete = false | ) |
Start a new thread in the detached state.
If you start the thread using this method then you cannot stop the thread execution, it will terminate by itself.
This method will return only after the initial() method has been executed.
- Parameters
-
selfDelete If set to true once the thread is terminated the object will be automatically destroyed.
- Exceptions
-
MCS_FATAL MSG_CALLING_PTHREAD_CREATE;
◆ state()
| int mcs::Thread::state | ( | ) |
◆ stop()
| void mcs::Thread::stop | ( | ) |
◆ test_cancel()
|
protected |
Member Data Documentation
◆ detached
|
private |
◆ lerror
◆ lid
|
private |
◆ lparent
|
private |
◆ lstate
|
private |
◆ lthrID
|
private |
◆ selfDelete
|
private |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: