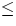 w is allowed if all values are positive,
but m < w is required if any values are negative.
If the number of
digits required to represent the integer datum exceeds w, then the
output field consists of a string of w asterisk (*)
characters.
w is allowed if all values are positive,
but m < w is required if any values are negative.
If the number of
digits required to represent the integer datum exceeds w, then the
output field consists of a string of w asterisk (*)
characters.
Logical data are encoded under format code Lw. Logical data are represented on output with the character T for true or F for false right justified in a blank-filled string of w characters. A null value may be represented by a completely blank string of w characters.
Integer data (including bit X and byte B type fields)
are encoded under format codes Iw.m,
Bw.m, Ow.m, and Zw.m. The
default value of m is one and the ``.m'' is optional. The
first letter of the code specifies the number base for the encoding
with I for decimal (10), B for binary (2), O for
octal (8), and Z for hexadecimal (16). Hexadecimal format uses
the upper-case letters A through F to represent decimal values 10
through 15. The output field consists of w characters containing
zero or more leading blanks followed by a minus if the internal datum
is negative followed by the magnitude of the internal datum in the form
of an unsigned integer constant in the specified number base with only
as many leading zeros as are needed to have at least m numeric
digits. Note that m 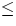 w is allowed if all values are positive,
but m < w is required if any values are negative.
If the number of
digits required to represent the integer datum exceeds w, then the
output field consists of a string of w asterisk (*)
characters.
w is allowed if all values are positive,
but m < w is required if any values are negative.
If the number of
digits required to represent the integer datum exceeds w, then the
output field consists of a string of w asterisk (*)
characters.
Real data are encoded under format codes Fw.d,
Ew.dEe, Dw.dEe,
ENw.d, and ESw.d. In all cases, the output
is a string of w characters including the decimal point, any sign
characters, and any exponent including the exponent's indicators,
signs, and values. If the number of digits required to represent the
real datum exceeds w, then the output field consists of a string of
w asterisk (*) characters. In all cases, d specifies the
number of digits to appear to the right of the decimal point. The
F format code output field consists of w-d-1 characters
containing zero or more leading blanks followed by a minus if the
internal datum is negative followed by the absolute magnitude of the
internal datum in the form of an unsigned integer constant. These
characters are followed by a decimal point (``.'') and d
characters giving the fractional part of the internal datum, rounded
by the normal rules of arithmetic to d fractional digits. For the
E and D format codes, an exponent is taken such that the
fraction 0.1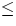 |datum|/10exponent<1.0.
The fraction (with appropriate sign) is output with an F format of width
w-e-2 characters with d characters after the decimal followed by an E
or D followed by the exponent as a signed e+1 character integer
with leading zeros as needed. The default value of e is 2
when the Ee portion of the format code is omitted. If
the exponent value will not fit in e+1
characters but will fit in e+2
then the E (or D) is omitted and the wider field
used. If the exponent value will not fit (with a sign character) in
e+2characters, then the entire w-character output field is
filled
with asterisks (*). The ES format code is processed in
the same manner as the E format code except that the exponent is
taken so that
|datum|/10exponent<1.0.
The fraction (with appropriate sign) is output with an F format of width
w-e-2 characters with d characters after the decimal followed by an E
or D followed by the exponent as a signed e+1 character integer
with leading zeros as needed. The default value of e is 2
when the Ee portion of the format code is omitted. If
the exponent value will not fit in e+1
characters but will fit in e+2
then the E (or D) is omitted and the wider field
used. If the exponent value will not fit (with a sign character) in
e+2characters, then the entire w-character output field is
filled
with asterisks (*). The ES format code is processed in
the same manner as the E format code except that the exponent is
taken so that ![]() . The EN format code is
processed in the same manner as the E format code except that
the exponent is taken to be an integer multiple of 3 and so that
. The EN format code is
processed in the same manner as the E format code except that
the exponent is taken to be an integer multiple of 3 and so that
![]() . All real format codes have number base
10. There is no difference between E and D format codes
on input other than an implication with the latter of
greater precision in the internal datum.
. All real format codes have number base
10. There is no difference between E and D format codes
on input other than an implication with the latter of
greater precision in the internal datum.
The Gw.dEe format code may be used with
data of any type. For data of type integer, logical, or character, it
is equivalent to Iw, Lw, or
Aw, respectively. For data of type real, it is
equivalent to an F format (with different numbers of characters
after the decimal) when that format will accurately represent the value
and is equivalent to an E format when the number (in absolute
value) is either very small or very large. Specifically, for real
values outside the range
![]() , it is
equivalent to Ew.dEe. For real values
within the above range, it is equivalent to
F
, it is
equivalent to Ew.dEe. For real values
within the above range, it is equivalent to
F![]() followed by
2+e blanks, where
followed by
2+e blanks, where
![]() and
and ![]() for
for
![]() if the real datum value lies in the range
if the real datum value lies in the range ![]() .
.
Complex data are encoded with any of the real data formats as described above. The same format is used for the real and imaginary parts. It is recommended that the 2 values be separated by a comma and enclosed in parentheses with a total field width of 2w+3.